A Natural Language Processing Approach to Grouping Students by Shared Interests
Main Article Content
Abstract
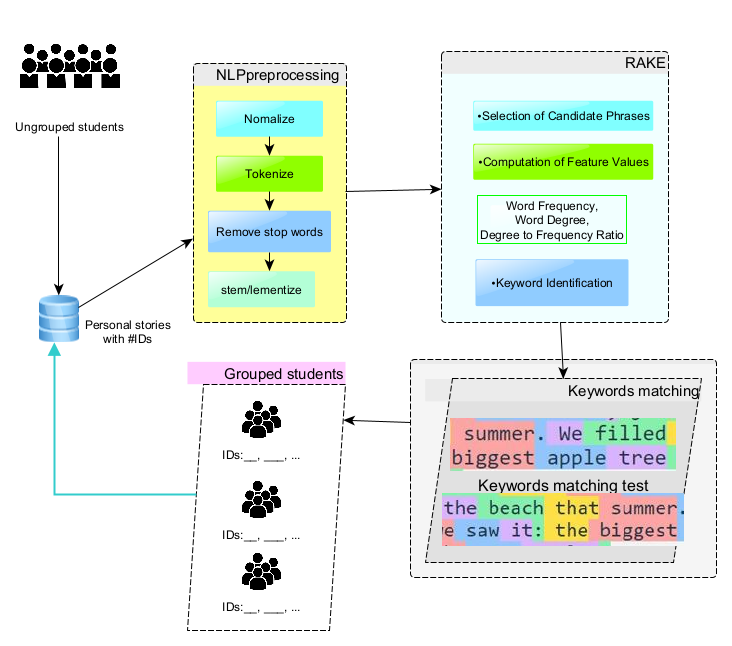
This research introduces an automated, Natural Language Processing (NLP)-based method for assembling students into groups based on shared interests, extracted from personal narratives. For the experiment, each student in the class was required to compose several stories, ranging from 300 to 400 words, to facilitate the extraction of common phrases. These phrases were then used to cluster students according to shared interests revealed in their personal stories. The study applied the Rapid Automatic Keyword Extraction (RAKE) algorithm, an unsupervised and language-agnostic technique for extracting keywords. This method is distinguished by its independence from specific linguistic structures, rendering it broadly applicable across various types of documents and fields. The RAKE algorithm operates through several distinct phases: The first phase involves removing all stopwords and phrase delimiters from the text. This step isolates potential key phrases within the narrative text. Contrary to the traditional use of TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency) metrics, RAKE employs a keyword score-matrix based on Word Frequency, Word Degree, and the Degree to Frequency Ratio. In the final phase, RAKE identifies the highest-scoring phrases among the phrase candidates. These phrases, representing the document's most significant themes or topics, are then used as the basis for student grouping, capturing the core interests manifest in the narratives.
Article Details
Public Licensing Terms
Thank you for your interest in our published work. We are committed to promoting open access and the free dissemination of knowledge. In line with this, we have established the following public licensing terms that govern the use and distribution of our published works:
-
Creative Commons License: All our published works are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA) license, unless otherwise specified.
-
Permissions Granted: a) Attribution: You are free to share and adapt the work, provided that you give appropriate credit to the author(s) and provide a link to the original source. b) NonCommercial: You may not use the work for commercial purposes without obtaining explicit permission from the copyright holder. c) ShareAlike: If you remix, transform, or build upon the work, you must distribute your contributions under the same CC BY-NC-SA license as the original work.
-
Compliance with License Terms: When using or distributing our published works, you must comply with the terms of the CC BY-NC-SA license and ensure that proper attribution is given to the original author(s).
-
Commercial Use: If you wish to use our published works for commercial purposes, you must seek permission from the copyright holder. Please contact us at [insert contact information] to discuss commercial licensing options.
-
Third-Party Rights: Our published works may contain third-party content or materials. The licensing terms for such content may vary, and you are responsible for complying with any additional terms or restrictions imposed by the respective copyright holders.
-
Disclaimer: The published works provided under these licensing terms are intended for informational and educational purposes only. We do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of the content, and we shall not be held liable for any errors, omissions, or damages arising from the use of the published works.
-
Termination: We reserve the right to terminate or modify the licensing terms for our published works at any time without prior notice. However, any works published prior to the modification or termination will continue to be governed by the original licensing terms.
By accessing, using, or distributing our published works, you acknowledge and agree to be bound by these public licensing terms. If you have any questions or require further clarification regarding the licensing terms or permissions, please contact us at permission@publications.dlpress.org
Last updated: 05-02-2023