Cloud-Based Biometric Authentication Techniques for Secure Financial Transactions: A Review
Main Article Content
Abstract
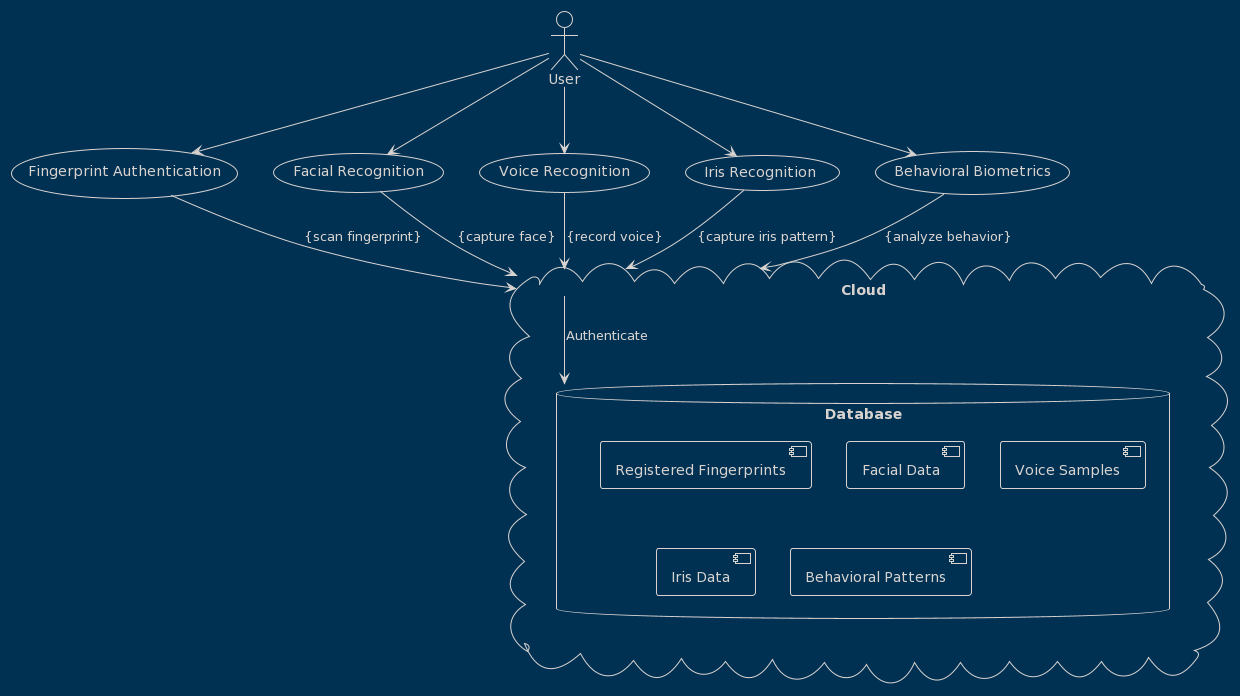
As financial transactions increasingly shift to online platforms, the need for robust authentication methods has become paramount. Cloud-based biometric authentication techniques have emerged as a promising solution to address security concerns and improve user experience. This research explores common cloud-based biometric authentication techniques, including fingerprint authentication, facial recognition, voice recognition, iris recognition, and behavioral biometrics. By leveraging cloud computing technology, these techniques provide a scalable, flexible, and secure environment for storing and processing biometric data and authentication algorithms. The research outlines the process of cloud-based biometric authentication for financial transactions, starting from the enrollment phase, where users securely register their biometric data. Subsequently, during an authentication request, the system captures biometric data through the user's device, encrypts it, and transmits it securely to the cloud server. The received biometric data is then matched against the pre-registered data stored in the cloud, and the system determines the authentication decision. If successful, the financial transaction is authorized, allowing users to proceed with their desired actions. Cloud-based biometric authentication offers several benefits for financial transactions, including enhanced security due to the difficulty of replicating biometric traits, convenience by eliminating the need to remember multiple passwords or PINs, reduced fraud risk, scalability to accommodate growing user bases, and real-time authentication capabilities.